|
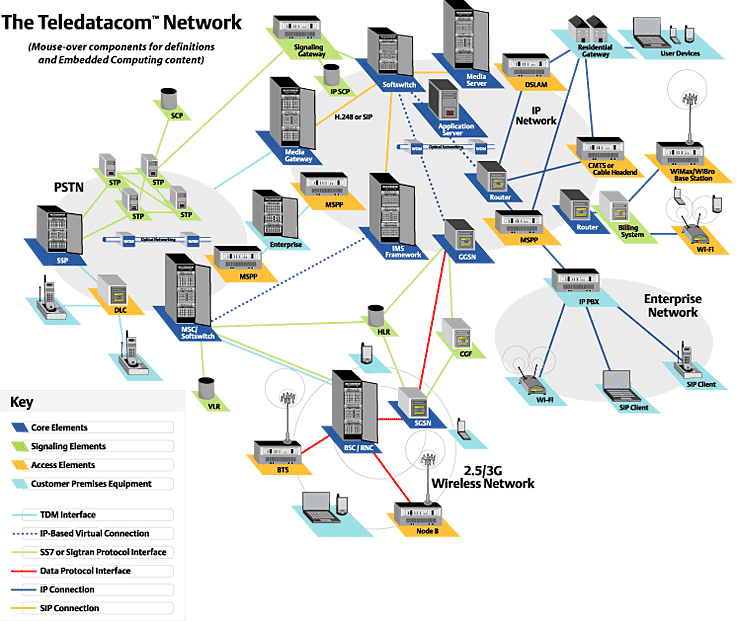
DLC (Digital Loop Carrier) - A
multiplexing/de-multiplexing system that typically has a high bandwidth
fiber connection to a Central Office out one side, and provides copper
interfaces to many residences out the other side. DLCís are deployed where
there is fiber installed to a neighborhood, but copper to the homes. DLCís
are less expensive to deploy than Fiber to the Home or Fiber to the Curb
because thereís only one optoelectric conversion required.
SSP (Service Switching Point)
- SSPs are switches that originate, terminate, or tandem calls. An SSP sends
signaling messages to other SSPs to setup, manage, and release voice
circuits required to complete a call. An SSP may also send a query message
to a centralized database (an SCP) to determine how to route a call (e.g., a
toll-free 1-800/888 call in North America). An SCP sends a response to the
originating SSP containing the routing number(s) associated with the dialed
number. An alternate routing number may be used by the SSP if the primary
number is busy or the call is unanswered within a specified time. Actual
call features vary from network to network and from service to service.
WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing)
- In fiber optic communications, a single laser beam can carry millions
of independent signals. A common way to get a large number of signals
onto a visible-light or infrared (infrared transmission) laser is to assign
each signal a separate radio frequency. At the fiber optic transmitter,
the laser is modulation at all signal frequencies simultaneously. At the
receiver, the signals are separated by a device similar to a radio receiver.
This process is frequency-division multiplexing (FDM).
STP (Signal Transfer Point) -
Signal Transfer Points communicate with SSPs on the SS7 network to set
up and tear down telephone calls. They also act as points to connect the
SSP and the SCP for services like 800 number translations.
SCP (Service Control Point) - An SCP is a database residing in the SS7 network
which is queried to determine how a call should be handled. For instance,
an SCP is consulted to provide the translation of an 800 number to an
actual phone number and to bill the owner of the 800 number for the call.
SCPs are physically separated from other components of the Intelligent
Network in order to make it easier to introduce new services.
Signaling Gateway - This gateway
routes calls between an IP network and a circuit switched network. It
is very similar to a Signal Transfer Point.
Softswitch - A softswitch is a central device in a telephone network which connects calls from one phone line to another, entirely by means of software running on a computer system.
Media Gateway - A media gateway
is a network element that provides conversion between the audio signals
carried on telephone circuits and data packets carried over the Internet
or over other packet networks.
Megaco (MEdia GAteway COntrol)
- Also referred to as H.248, it is a standard specifying the interface
between a Media Gateway Controller and Media Gateways.
Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity) - is
the popular term for a high-frequency wireless local area network (WLAN).
The Wi-Fi technology is rapidly gaining acceptance in many companies as
an alternative to a wired LAN. It can also be installed for a home network.
Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity) - is
the popular term for a high-frequency wireless local area network (WLAN).
The Wi-Fi technology is rapidly gaining acceptance in many companies as
an alternative to a wired LAN. It can also be installed for a home network.
DSLAM (Digital Subscriber Line Access
Multiplexer) - DSLAM is a network device, usually at a telephone
company central office, that receives signals from multiple customer Digital
Subscriber Line (DSL) connections and puts the signals on a high-speed
backbone line using multiplexing techniques. Depending on the product,
DSLAM multiplexers connect DSL lines with some combination of asynchronous
transfer mode (ATM), frame relay, or Internet Protocol networks. DSLAM
enables a phone company to offer business or homes users the fastest phone
line technology (DSL) with the fastest backbone network technology (ATM).
Residential Gateway - A VoIP gateway
designed for home and SOHO (Small Office/Home Office) use. Residential
gateways may include additional capabilities such as a firewall.
Cable Headend - A control center
of a Cable TV system, where incoming signals are amplified, converted,
processed, and combined into a common cable for transmission to customers.
Cable headends also provide high-speed internet access and data service.
PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network)
- PSTN (public switched telephone network) is the world's collection of
interconnected voice-oriented public telephone networks, both commercial
and government-owned. It's also referred to as the Plain Old Telephone
Service (POTS).
GGSN (Gateway GPRS Service Node)
- A system that acts as a data gateway between 2.5G and 3G mobile networks
and an IP network such as the Internet.
Router - On the Internet, a router
is a device or, in some cases, software in a computer, that determines
the next network point to which a packet should be forwarded toward its
destination. The router is connected to at least two networks and decides
which way to send each information packet based on its current understanding
of the state of the networks it is connected to.
Media Server - A device that processes
multimedia applications such as call distribution, fax-on-demand, and
automated e-mail response programs. Media Servers consolidate separate
communication devices, often resulting in reduced start-up costs, simplified
maintenance and administration, and increased application development
flexibility.
Billing System A system that
tracks customer usage of services, and calculates the impact on a customer's
account, based on the price of the services. Billing systems have come
to include non-core functionality such as customer management, integration
with payment gateways, and statistical analysis.
Optical Networking - The technology
associated with the transmission of information as light pulses along
a glass or plastic wire or fiber. Optical fiber carries much more information
than conventional copper wire and is in general not subject to electromagnetic
interference and the need to retransmit signals. Most telephone company
long-distance lines are now of optical fiber.
IP PBX (Internet Protocol Private Branch
eXchange) - An enterprise-scale telephone switch that enables users
of IP telephones (such as H.323 clients, SIP Clients, etc.) to make Voice
over IP telephone calls to other IP phones or phones on the public switched
telephone network. Most IP PBXs can also switch traditional voice traffic.
SIP Client - A Voice over IP-enabled
phone or computer program that uses the Session Internet Protocol (SIP).
SIP is a request-response protocol, dealing with requests from clients
and responses from servers. Participants are identified by SIP URLs. Requests
can be sent through any transport protocol, such as UDP, SCTP, or TCP.
SIP determines the end system to be used for the session, the communication
media and media parameters, and the called party's desire to engage in
the communication.
Enterprise Network - A network
for a large business enterprise.This kind of network may comprise a number
of local area networks which have to interface with each other as well
as a central database management system and many client workstations.
IP Network - A generic term used
to refer to any Internet Protocol (IP)-based network such as the Internet
or Ethernet Local Area Networks or private IP WIde Area Networks.
VLR (Visitor Location Register
- The VLR is a database that contains temporary information about subscribers
that is needed by the MSC in order to service visiting subscribers. The
VLR is always integrated with the MSC. When a mobile station roams into
a new MSC area, the VLR connected to that MSC will request data about
the mobile station from the HLR. Later, if the mobile station makes a
call, the VLR will have the information needed for call setup without
having to interrogate the HLR each time.
BTS (Base Transceiver Station)
- The Base Transceiver Station is the transmit and receive link for a
mobile communication system. It's the device that actually communicates
with the mobile phone. The BTS connects to a BSC over a T1/E1 line.
CGF (Charging Gateway Function)
- A billing system in the wireless networks.
HLR (Home Location Register) -
The Home Location Register (HLR) is the main database of permanent subscriber
information for a mobile network. The HLR is an integral component of
CDMA (code division multiple access), TDMA (time division multiple access),
and GSM (Global System for Mobile communications) networks. Maintained
by the subscriber's home carrier (or the network operator where the user
initiated the call), the HLR contains pertinent user information, including
address, account status, and preferences.
MSC (Mobile Switching Center)
- Also sometimes called a Mobile Telephone Switching Office (MTSO) or
Mobile Switching Office (MSO). A telephone switch, similar to a central
office switch, that bridges a mobile telephone network with another telephone
network such as the PSTN.
BSC (Base Station Controller)
- The BSC works with Base Transceiver Stations to act as a link between
wireless devices such as cell phones and the wireline telephone network.
RNC (Radio Network Controller) - Similar to a Base Station Controller but the term RNS is used in conjunction with wireless data services. An RNC works with Base Transceiver Stations to act as a link between wireless devices such as an internet-enabled mobile phone and the Internet.
RNC (Radio Network Controller) - Similar to a Base Station Controller but the term RNS is used in conjunction with wireless data services. An RNC works with Base Transceiver Stations to act as a link between wireless devices such as an internet-enabled mobile phone and the Internet.
SGSN (Serving GPRS Support Node)
- Second new functional element of the GPRS network.
Node B - A wireless base station
which provides the following functions: Air interface Transmission &
Reception, Modulation & Demodulation, CDMA Physical Channel coding,
Micro Diversity, Error Handing, Closed loop power control.
2.5/3G Wireless Network - Wireless
standards that allow from 64 to 384 kbits/s in a mobile environment and
up to 2 Mbits/s in an environment where the device is not moving. The
greater computing complexity of the 2.5/3G standards allows for better
usage of the available wireless spectrum, such as adaptive modulation
in the 2.5G Enhanced Data Rate for Global System for Mobile Communication
Evolution (Edge) standard, along with better error correction, such as
turbocoding in the 3G standards.
Multi Service Provisioning Platform. An access system that
can provision a
variety of different services such as TDM, Gigabit Ethernet, Wave Division
Multiplexing (WDM), or Packet over SONET (PoS), to the end user. Artesyn
provides Controller Boards and Line Cards to serve this application.
IP Multimedia Subsystem. A standard specified
by the 3GPP organization and
embraced by others, which defines a generic architecture for offering
VoIP,
and multimedia services in both wireless and wireline networks. An example
service provided by the IMS architecture includes voice, picture, text
and
video messaging. Artesyn offers controller boards and line card solutions
to serve this application.
WIMax/WiBro Base Station. Worldwide Interoperability for
MicroWave Access (WiMAX) / Wireless Broadband
(WiBro). WiBro is a wireless access technology developed by the Korean
telecom industry. WiBro basestations provide wireless access to data
networks, offering aggregate throughput of 30 to 50 Mbits/second and
cover a
radius of 1 to 5 kilometers. WiMAX is a similar technology defined by
the
IEEE 802.16 working group. WiMAX basestations can cover a radius of up
to
50 kilometers with line of sight access, but more realistically cover
a 15
kilometer radius without line of sight. Artesyn can provide controller
and
backhaul line card solutions for this application.
Application Server. A server in a distributed network that provides other systems or end
users execution resources for a defined set of applications.
| ©2007 Emerson Network Power, Embedded Computing. All rights reserved. design: Concentre Communications, Inc.® |
| Terms & Conditions | Privacy Policy | Job Recruiting | Site Map | |